Inductance may be made by winding a core of conductive material, typically copper wire, or the core may be removed or replaced with a ferromagnetic material. Core materials with higher permeability than air can bind the magnetic field more tightly around the inductance element, thus increasing the inductance. There are many types of inductors, most of which are made of outer layer enameled coils wrapped around ferrite spools, while some guard inductors embed the coils entirely inside the ferrite. Some inductor elements have adjustable cores. Thus, the inductance can be changed. Small inductors can be etched directly onto the PCB board using a method of laying spiral tracks. Low-value inductors can also be manufactured in integrated circuits using the same process used to make transistors. In these applications, aluminum interconnects are often used as conduction materials. Either way, the most widely used circuit based on practical constraints is called a "rotator", which uses a capacitor and an active element to exhibit the same properties as an inductor. Inductance elements used for high-frequency isolation are often composed of a wire passing through a magnetic column or bead.
Midget Inductor
A small fixed inductor is usually made by enamelled wire wound directly on the core, mainly used in filtering, oscillation, notch, delay, and other circuits. It has sealed and unsealed two types of packaging, both of which have vertical and horizontal two types of shape structure.
1. Vertical sealing fixed inductor. Vertical sealing fixed inductor adopts the same type pin, the domestic inductance range is 0.1~2200μH(directly marked on the shell), the rated working current is 0.05~1.6A, the error range is ±5%~±10%, the imported inductance, the current range is larger, the error is smaller. Imported TDK series color code inductor, its inductance with color points marked on the surface of the inductor.
2. Horizontal sealing fixed inductor. Horizontal sealing fixed inductor adopts axial pin, domestic has LG1, LGA, LGX series, etc.
LG1 series inductors range from 0.1 to 22,000 μH(directly marked on housing).
LGA series inductors are of ultra-small structure, similar in appearance to 1/2W color ring resistors, with inductance ranging from 0.22 to 100μH(marked with color ring on the housing), rated current from 0.09 to 0.4A.
LGX series color code inductors are also small package structure, the inductance range is 0.1 to 10000μH, rated current is 50mA, 150mA, 300mA and 1.6A four specifications.
Adjustable Inductor
Commonly used adjustable inductors include oscillating coils for semiconductor radios, line oscillating coils for TV sets, line linear coils, intermediate frequency trap coils, frequency compensation coils for audio, and wave blocking coils.
1. Oscillating coil for semiconductor radio: This oscillating coil forms a local oscillation circuit with a variable capacitor in a semiconductor radio, and is used to generate a local oscillation signal whose radio signal received by the input tuning circuit is higher than 465 kHz. The outside is a metal shield, and the inside is composed of a nylon lining frame, an I-shaped magnetic core, a magnetic cap and a pin seat, and a winding made of high-strength enameled wire is used on the I-shaped magnetic core. The magnetic cap is mounted on the nylon frame in the shield, which can be rotated up and down, and the inductance of the coil can be changed by changing the distance between it and the coil. The internal structure of the TV intermediate frequency trap coil is similar to that of the oscillation coil, except that the magnetic cap is adjustable.
2. Line oscillating coils for TV sets: Line oscillating coils were used in early black-and-white TV sets. It formed a self-excited oscillation circuit with peripheral resistance-capacitance elements and line oscillating transistors (three-point oscillator or intermittent oscillator, multivibrator), used to generate a rectangular pulse voltage signal with a frequency of 15625HZ.
There is a square hole in the center of the magnetic core of the coil, and the line synchronization adjustment knob is directly inserted into the square hole. Rotate the line synchronization adjustment knob to change the relative distance between the magnetic core and the coil, thereby changing the inductance of the coil and keeping the line oscillation frequency. For 15625HZ, the automatic frequency control circuit (AFC) sends the line synchronization pulse to produce synchronous oscillation.
3. Line linear coil: Line linear coil is a non-linear magnetic saturation inductance coil (its inductance decreases with the increase of current), it is generally connected in series in the line deflection coil loop, and its magnetic saturation characteristics are used to compensate the image quality. Linear Distortion.
The linear coil is wound on the "I" type ferrite high-frequency magnetic core or ferrite magnetic rod with enameled wire, and an adjustable permanent magnet is installed next to the coil. By changing the relative position of the permanent magnet and the coil to change the size of the coil inductance, so as to achieve the purpose of linear compensation.
Choke Inductor
A blocking inductor refers to an inductive coil used to block the AC current path in a circuit.
It is divided into high frequency choke coil and low frequency choke coil.
1. High-frequency choke coil: The high-frequency choke coil is also called a high-frequency choke coil, which is used to prevent the passage of high-frequency alternating current.
High-frequency choke coils work in high-frequency circuits, and mostly use hollow or ferrite high-frequency magnetic cores, the skeleton is made of ceramic materials or plastics, and the coils are made of honeycomb-type segmented winding or multi-layer flat-wound segmented winding.
2. Low-frequency choke coil: The low-frequency choke coil is also called a low-frequency choke coil. It is used in circuits such as current circuits, audio circuits or field output, and its function is to prevent the passage of low-frequency alternating current.
Usually, the low frequency choke coil used in the audio circuit is called the audio choke coil, the low frequency choke coil used in the field output circuit is called the field choke coil, and the low frequency choke coil used in the current filter circuit is called the field choke coil. It is called filter choke ring.
The low-frequency choke ring generally adopts "E"-shaped silicon steel core (commonly known as silicon steel core), permalloy core or iron core. In order to prevent the magnetic saturation caused by the large DC current, there should be an appropriate gap in the iron core during installation.
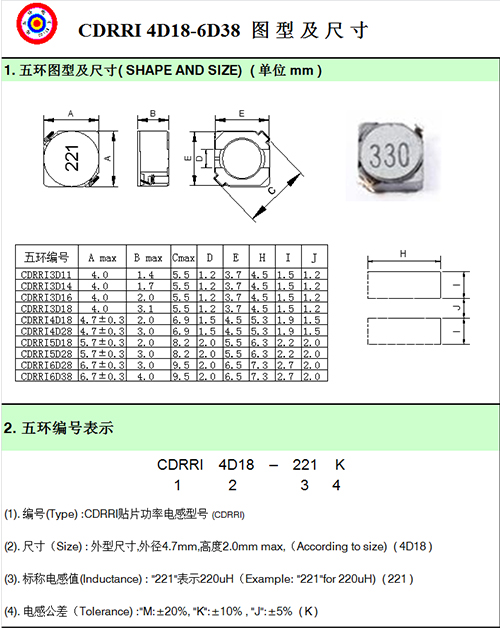
|
|
CDRRI3D11-3D28 Series Features |
|
|||||||||||
|
The five rings number |
L |
DC Resistance mΩ max direct current resistance |
Rated DC Current(A) max |
||||||||||
|
Part No |
u H |
||||||||||||
|
inductance |
3D11 |
3D14 |
3D16 |
3D28 |
|
|
3D11 |
3D14 |
3D16 |
3D28 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R5N |
1.5 |
|
76 |
52 |
|
|
|
|
2.6 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R2N |
2.2 |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.20 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-2R4N |
2.4 |
|
129 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.00 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R7N |
2.7 |
105 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.53 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-3R2N |
3.2 |
|
139 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.80 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 3R3N |
3.3 |
|
|
85 |
72.1 |
|
|
|
|
1.10 |
2.2 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-4R7N |
4.7 |
156 |
214 |
105 |
88.3 |
|
|
0.40 |
1.45 |
0.90 |
1.65 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 6R8N |
6.8 |
225 |
290 |
170 |
119 |
|
|
0.34 |
1.20 |
0.73 |
1.24 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-8R2N |
8.2 |
294 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 100N |
10.0 |
338 |
440 |
210 |
145 |
|
|
0.28 |
1.00 |
0.55 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-120N |
12.0 |
418 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 150N |
15.0 |
550 |
650 |
295 |
213 |
|
|
0.23 |
0.80 |
0.45 |
0.9 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-180N |
18.0 |
626 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 220N |
22.0 |
731 |
830 |
430 |
335 |
|
|
0.19 |
0.65 |
0.40 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-330N |
33.0 |
1108 |
|
675 |
481 |
|
|
0.17 |
|
0.32 |
0.58 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 390N |
39.0 |
1390 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 470N |
47.0 |
|
|
|
599 |
|
|
0.14 |
|
|
0.48 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRI4D18-6D38 Series Features |
|
|||||||||||
|
The five rings number |
L |
DC Resistance mΩ max direct current resistance |
Rated DC Current(A) max |
||||||||||
|
Part No |
u H |
||||||||||||
|
inductance |
4D18 |
4D28 |
5D18 |
5D28 |
6D28 |
6D38 |
4D18 |
4D28 |
5D18 |
5D28 |
6D28 |
6D38 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R0N |
1.0 |
45 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.72 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 1R2N |
1.2 |
|
23.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.56 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-1R8N |
1.8 |
|
27.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R2N |
2.2 |
75 |
31.3 |
|
|
|
|
1.32 |
2.04 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-2R6N |
2.6 |
|
|
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.6 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 2R7N |
2.7 |
105 |
43.3 |
|
|
|
|
1.28 |
1.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-3R0N |
3.0 |
|
|
|
24 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
2.4 |
3.0 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 3R3N |
3.3 |
110 |
49.2 |
|
|
|
20 |
1.04 |
1.57 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX-3R9N |
3.9 |
155 |
64.8 |
|
|
27 |
|
0.88 |
1.44 |
|
|
2.6 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 4R1N |
4.1 |
|
|
57 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.95 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-4R2N |
4.2 |
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 4R7N |
4.7 |
162 |
72 |
|
|
|
|
0.84 |
1.32 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-5R0N |
5 |
|
|
|
|
31 |
24 |
|
|
|
|
2.4 |
2.9 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 5R3N |
5.3 |
|
|
|
38 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.9 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-5R4N |
5.4 |
|
|
76 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.60 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 5R6N |
5.6 |
170 |
100.9 |
|
|
|
|
0.8 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-6R0N |
6 |
|
|
|
|
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.25 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 6R2N |
6.2 |
|
|
96 |
45 |
|
27 |
|
|
1.40 |
1.8 |
|
2.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX-6R8N |
6.8 |
200 |
108.9 |
|
|
|
|
0.76 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 7R3N |
7.3 |
|
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.1 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX-7R4N |
7.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
31 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.3 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 8R2N |
8.2 |
245 |
117.5 |
|
53 |
|
|
0.68 |
1.04 |
|
1.6 |
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-8R6N |
8.6 |
|
|
|
|
58 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.85 |
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 8R7N |
8.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
CDRRIXXX-8R9N |
8.9 |
|
|
116 |
|
|
|
|
|
1.25 |
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 100N |
10 |
200 |
128.3 |
124 |
65 |
65 |
38 |
0.61 |
1.0 |
1.20 |
1.30 |
1.7 |
2.0 |
|
CDRRIXXX-120N |
12 |
210 |
131.6 |
153 |
76 |
70 |
53 |
0.56 |
0.84 |
1.10 |
1.20 |
1.55 |
1.7 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 150N |
15 |
240 |
149 |
196 |
103 |
84 |
57 |
0.50 |
0.76 |
0.97 |
1.10 |
1.4 |
1.6 |
|
CDRRIXXX-180N |
18 |
338 |
166 |
210 |
110 |
95 |
92 |
0.48 |
0.72 |
0.85 |
1.00 |
1.32 |
1.5 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 220N |
22 |
397 |
235 |
290 |
122 |
128 |
96 |
0.41 |
0.7 |
0.80 |
0.90 |
1.2 |
1.3 |
|
CDRRIXXX-270N |
27 |
441 |
261 |
330 |
175 |
142 |
109 |
0.35 |
0.58 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
1.05 |
1.2 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 330N |
33 |
694 |
378 |
386 |
189 |
165 |
124 |
0.32 |
0.56 |
0.65 |
0.75 |
0.97 |
1.1 |
|
CDRRIXXX-390N |
39 |
709 |
383.7 |
520 |
212 |
210 |
138 |
0.30 |
0.50 |
0.57 |
0.70 |
0.86 |
1.0 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 470N |
47 |
|
587 |
595 |
260 |
238 |
155 |
|
0.48 |
0.54 |
0.62 |
0.8 |
0.95 |
|
CDRRIXXX-560N |
56 |
|
624.5 |
665 |
305 |
277 |
202 |
|
0.4 |
0.5 |
0.58 |
0.73 |
0.9 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 680N |
68 |
|
699 |
840 |
355 |
304 |
234 |
|
0.35 |
0.43 |
0.52 |
0.65 |
0.75 |
|
CDRRIXXX-820N |
82 |
|
914.8 |
978 |
463 |
390 |
324 |
|
0.32 |
0.41 |
|
0.6 |
0.7 |
|
CDRRIXXX- 101N |
100 |
|
1020 |
1200 |
520 |
535 |
358 |
|
0.29 |
0.36 |
0.42 |
0.54 |
0.65 |
|
CDRRIXXX-121N |
120 |
|
1270 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.27 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX- 151N |
150 |
|
1350 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.24 |
|
|
|
|
|
CDRRIXXX-181N |
180 |
|
1540 |
|
|
|
|
|
0.22 |
|
|
|
|